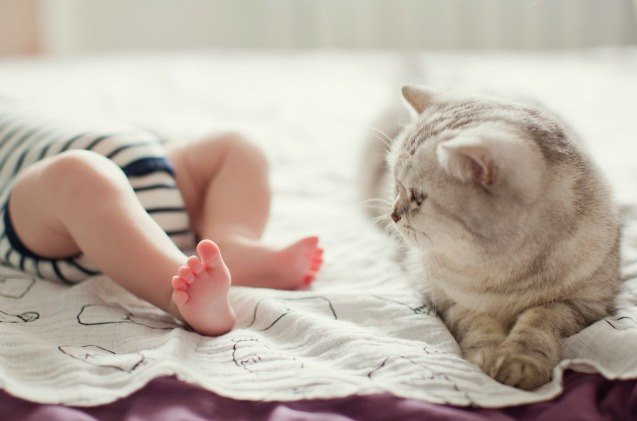
Study: Exposure to Cats Can Reduce Childhood Asthma Rates

Researchers from the Copenhagen Studies on Asthma in Childhood Research Center (COPSAC), Denmark, are suggesting that cats can prevent asthma from developing in children.
The scientists concluded that cats neutralize the effect of a specific gene in our body. When this gene is activated, children have double the risk of developing activated. They believe that if a cat is in the home when the child is born, the gene is never activated, and the risk of asthma decreases significantly.
Related: What is Cat Scratch Fever and How Can You Avoid Being Infected?
Hans Bisgaard is a professor of pediatrics and the head of COPSAC. He is also the lead author of the study and he says that he was surprised because the study showed that genes connected to diseases can be basically switched on or off like a light based on the environment we are in.
He says that it shows how the connection between our genetics and the environment is so important, and in particular, how important our environments are in pregnancy and a child’s early life.
The study looked at 377 Danish children whose mothers had asthma–looking at their mapped genes and information about their environments and upbringing with both surveys and samples. They found that cats removed the risk of asthma developing in children who had a specific variation of the gene 17q21, also called TT. This gene has the strongest impact on whether the children would develop asthma or not and almost one in three of the children carried the TT variation gene. Their mother having asthma or not had no bearing on that statistic.
The scientists found that only cats seemed to make a difference in the development of asthma in children who had the TT gene variation, and exposure to dogs early in life did not have the same effect. More, they also believe that cats helped protect against asthma and bronchitis, as the 17q21 gene is connected to those conditions.
Related: Study: Pets Help Lower The Risk Of Childhood Asthma
Because these results show that genes and the environment interact so precisely and yet in such unknown ways, it’s important for more research to be done to look at the broader implications. Particularly because the study doesn’t show exactly what it is about cats, and whether it is cat specific, that helps protect children with those gene variations, the researchers would like to know exactly what kind of and how much exposure to cats early on would make an impact.
Co-author Jakob Stokholm believes that it could be something in the bacteria that cats carry or something about fungus or viruses specific to cats that children are then exposed to that can influence the immune system. Stokholm says that this could lead the way for finding more about how to protect children from developing asthma altogether.

More by Lori Ennis